Provisioner Import
The Provisioner Import page allows you to extend Super.Human.Installer (SHI) with custom provisioners by importing them from various sources.
Access this page via Settings -> Import Provisioner.
Overview
Custom provisioners enable you to define and share specialized server environments beyond the built-in HCL Domino types. This page provides multiple methods for adding these custom provisioners to your SHI application, making them available for selection when creating new servers.
Import Methods
The page offers three different import methods through a tabbed interface:
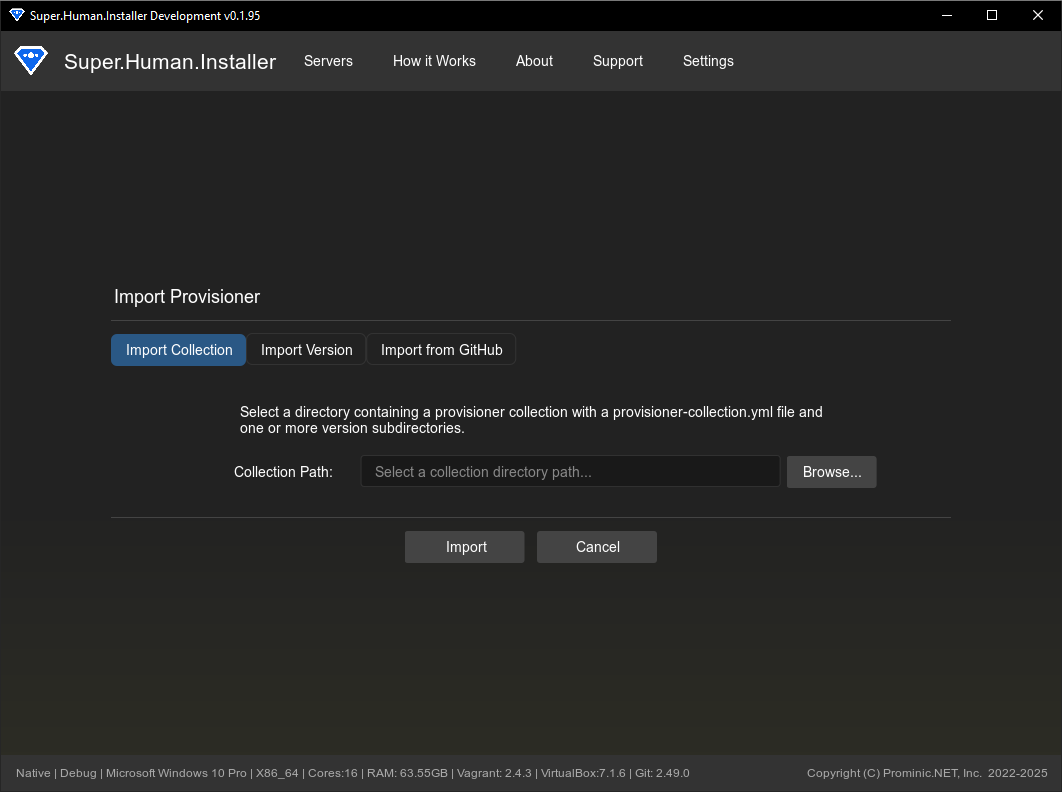
1. Import Collection (Local Directory)
Use this tab to import a complete provisioner collection from a directory on your computer.
- Requirements: The selected directory must contain:
- A
provisioner-collection.ymlfile defining the collection metadata (name, type, description). - One or more version subdirectories (e.g.,
1.0.0,1.1.0). - Each version subdirectory must contain a
provisioner.ymlfile defining version-specific metadata (roles, configuration fields) and any necessary template/script files.
- A
- Process: Click “Browse…”, select the root directory of the collection, and click “Import”. SHI copies the entire structure into its internal
provisionersdirectory. - Use Case: Importing a complex provisioner with multiple versions defined.
2. Import Version (Local Directory)
Use this tab to import a single, specific version of a provisioner from a directory on your computer.
- Requirements: The selected directory must contain:
- A
provisioner.ymlfile defining the version’s metadata (including itstype). - Any necessary template/script files for this specific version.
- A
- Process: Click “Browse…”, select the directory containing the specific version, and click “Import”.
- If a collection for the
typedefined inprovisioner.ymlalready exists in SHI’sprovisionersdirectory, this version will be added as a new subdirectory. - If no collection exists for that
type, a new collection directory and a basicprovisioner-collection.ymlwill be created automatically based on the version’s metadata.
- If a collection for the
- Use Case: Adding a new version to an existing provisioner collection or importing a single-version provisioner.
3. Import from GitHub
Use this tab to import a provisioner directly from a GitHub repository.
- Organization/User: The GitHub username or organization owning the repository (e.g.,
prominic). - Repository: The name of the repository (e.g.,
provisioner-example). - Branch: The specific branch to import (defaults to
main). - GitHub Token: (Optional) Select a pre-configured Git API Token/PAT from your Secrets Management to access private repositories. Leave as “None” for public repositories.
- Download Method:
- Git Clone (Checkbox Enabled): Uses
git cloneto download the repository. This method supports private repositories (with a token) and handles submodules correctly. This is the only method currently supported for asynchronous background import. - HTTP (Checkbox Disabled): [Note: While the UI toggle exists, the underlying asynchronous import currently only functions with Git Clone enabled.]
- Git Clone (Checkbox Enabled): Uses
- Process: Fill in the details and click “Import”.
- If “Git Clone” is selected, the import runs asynchronously in the background. A spinner indicates progress, and a notification appears upon completion (success or failure).
- SHI clones the repository to a temporary location, searches for a valid provisioner structure (either a collection or a single version at the root or in common subdirectories like
provisioner/or a folder matching the repo name), and imports it using the same logic as the local import methods.
- Use Case: Easily importing provisioners shared on GitHub.
After Import
Once a provisioner is successfully imported (either locally or from GitHub):
- It becomes available for selection on the Service Type screen when creating a new server.
- Servers created with it will use its defined roles, configuration fields, templates, and scripts.
Troubleshooting Import Failures
- Local Imports:
- Ensure the selected directory has the correct structure and required metadata files (
provisioner-collection.ymland/orprovisioner.yml). - Check file system permissions for the source directory and SHI’s
provisionersdirectory.
- Ensure the selected directory has the correct structure and required metadata files (
- GitHub Imports:
- Verify the Organization, Repository, and Branch names are correct.
- Ensure the repository contains a valid provisioner structure at the root or a common subdirectory.
- For private repositories, confirm the selected GitHub Token is valid and has read access.
- Check network connectivity.
- Ensure Git is correctly installed and accessible in your system’s PATH.
- Review SHI’s logs (
<AppStorage>/logs/current.txt) for detailed error messages from thegit cloneprocess.
Relevant Files
- Source/superhuman/components/ProvisionerImportPage.hx - UI implementation.
- Source/superhuman/managers/ProvisionerManager.hx - Core import logic (local and GitHub async).
- Source/superhuman/server/definitions/ProvisionerDefinition.hx - Data structure for provisioners.
- Genesis/Source/prominic/sys/applications/git/Git.hx - Git command wrapper used for GitHub imports.
- Genesis/Source/prominic/sys/io/Executor.hx - Handles asynchronous command execution.